SOLUTION BRIEF
Segmenting all Cloud Workloads
Cloud architects understand that one of the basic foundations of an effective security framework within the cloud is the appropriate segmentation of applications. With proper segmentation across multiple layers, L3 to L7, you can isolate business-critical applications from potential network threats and also control the directionality of traffic, so that lateral movement across the network is reduced. While it’s imperative for organizations to have proper segmentation in their networks today, they struggle to obtain the right set of tools and solutions to implement the right segmentation policies.
If you’re evaluating application segmentation solutions, this solution brief is for you.
BY CHINEDU EGONU
Application segmentation is the practice of creating secure boundaries around individual applications or services and controlling access to/from them using policies. Access control using policies ensures that only authorized endpoints (other applications or user devices) can communicate with the individual applications or services. Policies are created using a wide variety of L3 to L7 parameters.
The practice has become popular in recent years given the changes in the threat landscape and rise in cyber attacks, especially as more applications are being moved to the cloud. Organizations typically implement application segmentation as part of their Zero Trust security framework and use the practice to mitigate threats to business-critical applications running in the network.
Segmentation in the Current Day
Today’s Enterprise IT environments contain a healthy mix of both traditional applications with legacy monolith designs and modern applications, (with fragmented microservices-based architectures, PaaS, SaaS) distributed across the cloud providers’ regions and DC environments.
When these corporate applications were concentrated in the data center, enterprise IT typically implemented segmentation via traditional L2/L3 technologies, i.e. VLANs, network CIDRs, virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) tables, access control lists (ACLs), etc.
However, as these corporate application are being deployed and consumed within the cloud, organizations typically seek these technologies either via tools native to cloud provider environments i.e., network security groups (NSGs), CIDRs within VPCs/VNETs, private links, or from 3rd-party solutions from MCN or ZTNA vendors which run in the cloud to implement their segmentation policies.
Organizations have realized that using traditional segmentation technologies are insufficient in implementing proper segmentation effectively within the cloud. NSGs and ACLs are very good at segmenting networks but are not ideal for specific application-to-application segmentation requirements. Additionally, segmentation in the cloud requires managing multiple security tables in multiple VPCs/VNETs across multiple regions and DCs. Many organizations today use thousands of VPCs/VNETs in the cloud to run hundreds of IaaS/Paas or containerized applications. In addition, IP addresses in the cloud constantly change so applying policies based on layer3/IPs makes is not relevant to the cloud and with rapid increases in services and modern arch (K8/service ), IPs will change and you have to constantly adjust policies. This is quite difficult to manage, especially with modern workloads (PaaS, containerized applications), and will worsen as the network continues to scale.
While VRF tables offer a slight improvement in implementing segmentation in the cloud, they don’t make it any easier to segment traditional or modern workloads at the application layer.
To implement app-to-app segmentation, some MCN vendors recommend that you move the application into separate VPCs/VNETs which adds to existing VPC management requirements and increases operational complexity.
Some vendor solutions even require network traffic to be routed to their external NaaS cloud for segmentation policies to be enforced. This approach is not only inefficient but potentially requires the organization to incur egress costs when traffic is routed to the external cloud.
An organization with tens of thousands of applications soon realizes it is impractical to use this approach. They will need to configure, deploy, and manage these agents across multiple regions, multiple clouds, and data centers.
The agent-based solutions also don’t address overlapping IP address situations. Tagging the application and modifying its IP routing tables are insufficient.
App-to-App segmentation requirements
It’s clear that implementation of app-to-app segmentation using network-layer technologies is not only impractical but increases complexity as network scales in the cloud. Applications, either traditional or modern, communicate with each other not only with IP addresses and port numbers but also using fully qualified domain names(FQDN), SNI headers, tokens, and other forms of L7 metadata. As such, any application-layer segmentation policy(the premise behind micro-segmentation) should contain parameters that include these metadata.
Organizations planning to implement app-to-app segmentation within their network should look for solutions which:
#1
Leverage cloud-native tools for connectivity and networking to traditional and modern workloads anywhere in the cloud.
#2
Can detect l7 metadata from application traffic. These will serve as parameters to build policies.
#3
Enforce segmentation policies consistently across clouds and DCs.
#4
Can scale across regions and clouds easily and quickly.
#5
Simplify operations and provide deep app-level insights.
App-to-App Segmentation using Prosimo
The Prosimo platform enables organizations to build and enforce segmentation policies across multiple players of the networking stack. The platform enables seamless integration of any application endpoint (container, IaaS, PaaS), routes traffic based on SNI headers, and enforces security policies using L7 metadata. At L7, traffic can be routed based on host headers or even restricted using a particular HTTP message type. Also, being able to enforce policies at L7 means you need not worry about overlapping network CIDRs as each application is uniquely identified using other attributes.
Organizations can segment their individual workloads across their cloud regions and DCs using policies they configure on the platform. These policies are propagated across the Prosimo fabric and are enforced by edge gateways deployed in regions within their cloud environment.
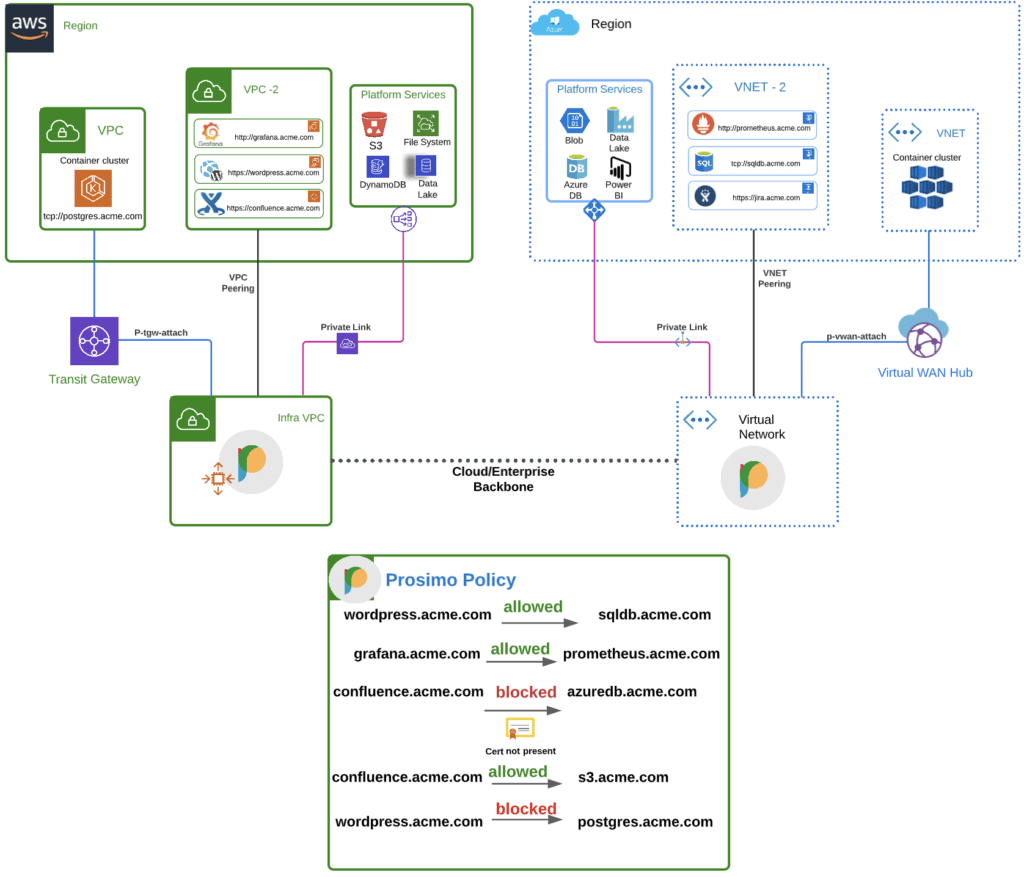
Key Features and Capabilities
Does not require applications to be moved to separate VPC/VNET or a software agent to be installed inside of the application.
Sets up Private link and NLB endpoints to establish transit which connects application endpoints or service ( FQDNs, PaaS, Serverless applications).
Extends regional construct like private link to connect to applications in any region or cloud, including DCs.
Creates and manages Private hosted zones in Route 53 to attract traffic at DNS layer from source VPCs to targets.
Creates a segment around each and every application/FQDN and allows authorized access strictly based on policies.
Use Prosimo Policy engine to enforce application (APIs, application ids & URIs) layer segmentation consistently across the hybrid multi-cloud environment.
Provides L7 visibility and insights such as, total response time at the HTTP layer and break down at each hop ( Cloud ingress, backbone, application VPC).
Summary
Prosimo platform’s application segmentation capabilities enable organizations to effectively segment their individual applications across cloud regions and DCs. Organizations can implement comprehensive segmentation policies consistently across their environment and ensure the directionality of traffic for not only authorized network segments but also for applications including both traditional and modern workloads.
