How Can You Ensure Network Security If You Don’t Control The Network?

In today’s complex landscape of multi-cloud operations, businesses face significant challenges with managing data exfiltration and countering malicious traffic spanning multiple cloud service providers. The lack of visibility, control, and robust network security in these environments makes them vulnerable to advanced threats. Cybercriminals globally are constantly devising new ways to bypass traditional security protocols, putting […]
Cloud Migration With AI: A Seamless Transformation

In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses are always looking for new ways to work smarter and more securely. Cloud migration stands out as a major breakthrough in this effort, enabling companies to transfer their operations and data to cloud-based platforms. But the real game-changer comes when businesses combine cloud migration with Artificial Intelligence (AI). This […]
How Should I Filter Egress Traffic From AWS VPCs?

As we all know, AWS follows a “Shared Responsibility Model” for security and compliance. This means that while AWS takes care of the security of the cloud itself, you are responsible for securing your data in the cloud. When it comes to securing Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), cloud operations teams usually focus on blocking unwanted […]
How To Manage Overlapping IP Addresses?

The swift advancement of cloud infrastructure has introduced fresh challenges, notably the issue of overlapping IP addresses and CIDR blocks. This issue mainly occurs in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, where there is no central system for assigning unique network spaces. As a result, connectivity issues arise across various organizational networks. Navigating the Challenge of Overlapping […]
When to Use Multi-Cloud vs. Single Cloud Solutions

Navigating the tech landscape often leads to the pivotal decision between single cloud and multi-cloud solutions. With digital transformation at the forefront, organizations must choose wisely to shape their IT infrastructure’s future. Let’s dive into these two cloud paradigms, comparing their differences, security concerns, and the journey from single to multi-cloud. Single Cloud Single cloud […]
What Is The Role Of Cloud Computing In Disaster Recovery?

Imagine you are working on an important task, and suddenly, you lose access to your crucial data and applications. This kind of interruption can halt your business operations instantly. For any business, big or small, such disruptions lead to more than just downtime—they can result in losing valuable customers and significant revenue. The modern solution […]
How To Identify And Block Threats With A Secure Cloud Network

As we maneuver through the complexities of the digital world, the security of our cloud network becomes more than just a priority—it’s essential for protecting what matters most to us. Whether you’re a business owner, IT professional, or just someone concerned about data privacy, recognizing and neutralizing threats is key to keeping your information safe. […]
Benefits Of Adopting A Multi-Cloud Approach For AI Deployment

In today’s world, people interact daily with software and digital services through the cloud. The cloud empowers developers to deliver cost-effective projects, reliable applications, and secure solutions. However, in the era of AI, exploring multi-cloud strategies is crucial. Implementing a multi-cloud approach allows a company to optimize its spending and enhance efficiency. Additionally, leveraging multiple […]
How Do You Manage A Multi Cloud Environment?

Using a multi-cloud approach helps businesses avoid being locked into one vendor, take advantage of the best technologies from different clouds, and save on costs by picking the most affordable cloud services for each need. Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Data Management Ensure Data and Application Portability Data silos and lack of portability are major issues […]
Why Multi-Cloud is Essential for Modern Enterprises

In today’s rapidly evolving enterprise landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a cornerstone of IT infrastructure. As enterprises transition their applications and data to the cloud, the shift toward multi-cloud architecture has become increasingly prominent. This blog post delves into why multi-cloud architecture is vital, its various types, benefits, and a real-world example to illustrate […]
The Impact Of Machine Learnings On Optimizing Multi-Cloud
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses increasingly rely on multi-cloud environments to enhance their operations, improve flexibility, and ensure data security. As the complexity of managing multiple cloud platforms grows, the role of machine learning (ML) in optimizing multi-cloud networks has become indispensable. This article delves into the ways machine learning is revolutionizing multi-cloud […]
How AI Enhances User Experience In Multi-Cloud Platforms

In today’s digital age, multi-cloud platforms are becoming increasingly popular for businesses looking to optimize their operations and improve flexibility. These platforms allow organizations to use multiple cloud services from different providers, creating a more versatile and resilient infrastructure. However, managing multiple cloud environments can be complex and challenging. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) […]
What Are The Benefits Of Cloud Computing?

Cloud computing involves delivering computing services over the internet, encompassing storage, servers, databases, software, and more. Its popularity has skyrocketed in recent years, thanks to its myriad advantages. Organizations worldwide have reaped significant benefits from cloud computing. If you’re considering a career in this field, it’s essential to understand the perks of cloud computing and […]
5 Benefits Of Using A Cloud Networking Service

Cloud networking services have the potential to completely transform the way your company functions. This innovative technology provides numerous advantages that can elevate your business to unprecedented levels of productivity, flexibility, and market viability. If you’ve been uncertain about integrating cloud networking solutions into your operations, keep reading. We’ll delve into the ways in which […]
How Does Multi-Cloud Work?

Embracing a multi-cloud strategy involves leveraging a variety of public cloud services from different providers. This approach isn’t just about diversifying resources; it’s a deliberate method to blend on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud frameworks, alongside edge computing. This integration allows organizations to consistently build, operate, and secure their applications across various environments. The drive […]
Best Practices For Data Privacy In Multi-Cloud Environments

In today’s digital world, many organizations use multiple cloud services to store and manage their data. This approach, known as a multi-cloud environment, offers numerous benefits but also presents unique challenges, particularly concerning data privacy. To ensure data remains secure and private across various cloud platforms, it is crucial to follow specific best practices. Here […]
What Is The Difference Between Cloud Computing And Cloud Networking?

Adopting cloud technology can streamline your company’s digital transformation. The cloud offers computing systems and IT services over the internet, eliminating the need for on-site computer services. This not only saves your business time and resources but also enhances scalability. Additionally, it allows for easier access to data and applications from anywhere. However, it’s crucial […]
Why Multi-Cloud Is The Future?

Modern enterprises are increasingly adopting multicloud architectures, utilizing multiple cloud providers to enhance their operations. Cloud Trends Report reveals that 90% of organizations now operate in multi-cloud environments, highlighting its widespread adoption.The demand for multicloud skills is soaring, as these capabilities enable companies to optimize infrastructure across various platforms and position resources and applications closer […]
Is Multi-Cloud The Same As Hybrid Cloud?
Defining the difference between hybrid cloud and multi-cloud can be challenging, as these terms are often used interchangeably. However, despite their similarities, there is a key distinction. In a multi-cloud setup, an enterprise leverages multiple public cloud services, typically from various providers. For instance, a company might run its web front-end application on one provider […]
Why Adopt A Multi-Cloud Strategy?

A multi-cloud strategy stands out as a robust approach enabling organizations to tap into the diverse capabilities offered by multiple cloud providers. It proves particularly beneficial for businesses aiming to segment their workloads among providers offering more cost-effective solutions for specific tasks, such as data analytics or database management. By leveraging the strengths of different […]
Why Choose Cloud Networking?

Nowadays, almost every business relies on cloud technology to some extent. Cloud networking offers scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to expand their infrastructure as needed. It also saves costs since companies only pay for the services they use. This article will explain cloud networking and cloud computing, their types, and the benefits for small and […]
What Is Multi Cloud Security?

In today’s digital age, mastering multicloud security is crucial for businesses. To get a grasp on this, we first need to define multicloud and hybrid cloud services. Multicloud involves utilizing cloud services from multiple providers, allowing your business to manage different projects across various cloud environments efficiently. Hybrid cloud, on the other hand, also employs […]
Why Do Companies Use Multi-Cloud?

As the cloud computing landscape grows, more companies are adopting multi-cloud strategies. This approach allows businesses to move workloads between cloud providers or across hybrid setups, leading to cost savings and the ability to leverage multiple clouds for specific needs. In 2023, over 90% of organizations are expected to use cloud services in some form. […]
What Is Cloud Computing?

Cloud computing is revolutionizing how we access and manage digital services, offering on-demand delivery of a vast array of computing resources. These include servers, storage solutions, databases, networking capabilities, software, and analytics. Instead of relying on traditional proprietary hard drives or local storage devices, cloud-based storage allows for remote saving and access, enhancing flexibility and […]
Overcoming the Challenges of Multi-Cloud Environments

The trend toward cloud migration is clear as more organizations shift from traditional data centers to the leading trio of cloud providers: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). IT chiefs are keen to propel their businesses forward with cloud-native apps, services, and infrastructure rather than exhausting resources on the upkeep […]
Why Is A Multi-Cloud Approach Gaining Such Popularity?

In today’s business landscape, the concept of “the cloud” is evolving rapidly, rendering the term somewhat outdated for many enterprises. Recent research from 451 Research reveals that a significant 70 percent of organizations are actively leveraging a variety of cloud services. Moreover, a notable 37 percent of these enterprises have embraced hybrid cloud technology, facilitating […]
What Is Cross-Cloud?

Cross-cloud is a term in cloud computing that refers to the ability to smoothly run applications and manage workloads across different cloud service providers (CSPs). The idea of “cross-cloud” came about with the rise of multi-cloud strategies. This strategy involves using a mix of public, private, and edge clouds, along with on-site infrastructure, to manage […]
What Are The Benefits Of Multicloud Strategy?

Embracing a multi-cloud strategy presents a formidable opportunity for organizations aiming to capitalize on the diverse offerings of various cloud providers. This approach enables businesses to strategically distribute their workloads among multiple cloud platforms, optimizing for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For instance, specific tasks such as data analytics or database management might find a more economical […]
Why Are Organizations Opting For A Multi-Cloud Approach?

Many businesses today opt for multicloud solution, driven by diverse needs and challenges. When an enterprise operates across various global regions, it often finds that a single public cloud provider cannot fully address its complex requirements. For such organizations, adopting a multicloud approach becomes an evident choice.Indeed, many businesses that incorporate public cloud services typically […]
How Does Multi-Cloud Improve Security?

Almost every organization (98% to be exact) that uses cloud computing is now using multi-cloud setups, as found in a recent Oracle study. As cloud technology rapidly changes, organizations must also update their security measures to protect their cloud setups. Strong multi-cloud security is essential to guard against cyber threats and breaches. Understanding Multi-Cloud Security […]
7 Reasons Multi-Cloud Infrastructure Is The Future Of IT Enterprise

As more and more businesses look to the future, they’re finding that using just one cloud isn’t enough. Instead, they’re turning to something called multi-cloud. This means using different types of clouds, like public, private, and hybrid, all at the same time. Why are businesses making this change? Well, it could be because of specific […]
What Are The Top 10 Benefits of Multi-Cloud?

In the fast-evolving landscape of business cloud computing, the spotlight often shines on private, public, and hybrid clouds, leaving multi-cloud strategies in the shadows. But it’s time to shed light on this transformative approach. Multi-cloud architecture, weaving together public, private, and hybrid cloud services, emerges as a savvy investment path for numerous enterprises, particularly those […]
What Are The Advantages Of Cloud Networking?

In the ever-evolving landscape of digital technology, the cloud has emerged as a cornerstone of modern infrastructure. Its omnipresence is no longer a novelty but a necessity for seamless operations in the digital realm. While cloud adoption has predominantly been associated with software accessibility and application hosting, its potential extends far beyond mere convenience. Enter […]
Networking announcements from GoogleNext show the value has moved up the stack. What is still missing?
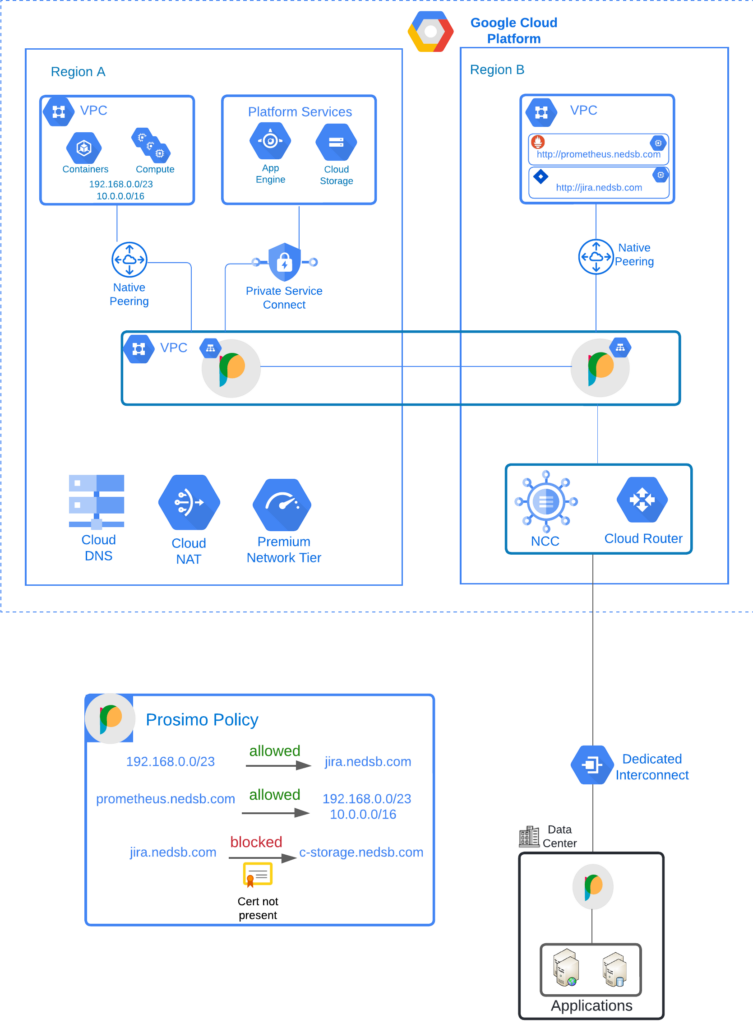
Google Next 2024 commenced this week, and it’s evident that the following three key themes are at the forefront for announcements around GCP networking services. The rise of service layer networking: Several enterprises are adopting a new operating model that moves networking to the application or service layer, eliminating the complexities associated with traditional IP […]
What Is Multi-cloud?

Multi-cloud refers to an IT strategy that leverages multiple cloud services from various providers. Instead of relying solely on a single vendor, organizations can choose the best cloud solutions for specific needs across different public clouds, private clouds, or even on-premises infrastructure. This approach offers greater flexibility, scalability, cost optimization, and vendor independence compared to […]
Is Multi-Cloud A Good Idea?

Multi-cloud, the use of multiple cloud providers, is gaining traction as organizations seek agility, cost optimization, and access to diverse services. But is it the right choice for everyone? This exploration delves into both the advantages – flexibility, improved redundancy, and potential cost savings – and the challenges – increased complexity, vendor lock-in risk, and […]
What Are The Advantages Of Multi-Cloud?

In today’s dynamic technological landscape, relying on a single cloud provider can limit your organization’s agility, innovation, and efficiency. Enter the multi-cloud approach, a strategic deployment across multiple cloud environments – public, private, or hybrid. This outline explores the key advantages of multi-cloud, equipping you to make informed decisions for your organization’s cloud journey. Advantages […]
What Is The Use Of Multi Cloud?

In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, multi-cloud has emerged as a strategic approach for businesses seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure and unlock new possibilities. It involves leveraging the unique strengths and capabilities of multiple cloud providers, creating a hybrid environment that best suits their specific needs and goals. This dynamic approach has gained […]
Is Multi Cloud Secure?

Multi-cloud adoption is rapidly growing, driven by the benefits of flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness it offers. However, concerns around security loom large, posing a major hurdle in widespread adoption. This article delves deep into the world of multi-cloud security, exploring its inherent advantages, potential vulnerabilities, and best practices for achieving a robust security posture. We’ll […]
What Is The Difference Between Cloud And Multi-Cloud?

The digital landscape is increasingly reliant on cloud computing, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, navigating the different cloud options can be confusing. This outline explores the key distinctions between “cloud” and “multi-cloud,” empowering you to make informed decisions for your IT needs. Choosing the Right Path: Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud Organizational Needs: This is the […]
What Are The Four Types Of Cloud Networking?
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cloud networking has emerged as a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure, offering unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. At its core, cloud networking refers to the interconnectivity of cloud services, applications, and resources over the Internet. It encompasses the hardware and software components, including servers, storage, network devices, and virtualized […]
What Are Cloud Services In Networking?
Cloud services have revolutionized how businesses and individuals approach data storage, processing, and general computing needs. This shift has significant implications for networking, altering how information is accessed, shared, and secured. Definition of Cloud Services Cloud services refer to a wide range of services delivered on-demand to companies and customers over the Internet. These services […]